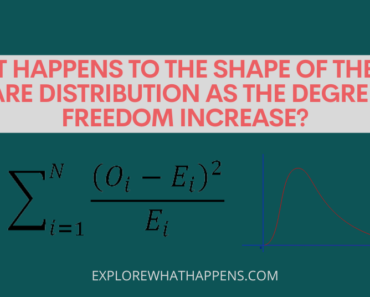
Too much [h+] in the environment can lead to environmental problems like water shortages, soil erosion, etc. But what happens when the [h+] in a solution decreases? According to scientists at the University of Utah, this leads to a decrease in the [oh–] ion. As a result, the solution becomes more alkaline, negatively affecting plant and animal life. In this post, we explore how this phenomenon works and what it means for our environment.
![As the [h+] in a solution decreases, what happens to the [oh–]?](https://explorewhathappens.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/As-the-h-in-a-solution-decreases-what-happens-to-the-oh–.png)
What would happen if we put our hand in a solution with a pH of 10? It would dissolve our hands in seconds. Well, in fact, it’s a little more complicated than that.
The concentration of OH- increases because the product of pKa and H+ concentration is constant, meaning that the concentration of OH- increases as the pH of the solution decreases.
If the pH is lower than 7, the hydrogen ion concentration is higher than the hydroxide ion concentration. That means the hydrogen ions are more dominant than the hydroxide ions. Since hydrogen ions have a positive charge, they are attracted to any negatively charged substance. The hydroxide ions, on the other hand, have a negative charge. So when the pH is lower than 7, they are more attracted to the positively charged substance. In this case, the positively charged substance is the hydrogen ions.
This means that at low pH, you can get a chemical reaction between the hydrogen ions and the hydroxide ions. In other words, you can create hydrogen gas when the pH is below 7. When we are talking about the pH of solutions, we are usually talking about the pH of pure water, which is 7. Pure water has a pH of 7. This means the hydrogen ion concentration is equal to the hydroxide ion concentration.
So, if you are dealing with a solution with a pH of 5 or lower, you should be aware that you can have a chemical reaction between the hydrogen ions and the hydroxide ions. This can cause you to release a lot of hydrogen gas into the air.
In fact, you can blow up a balloon in a closed room, and most of the hydrogen is released during the inflation process.