One of the most common questions asked in chemistry is what happens when an element is artificially transmuted. This process of changing one element into another is called transmutation and it can be broken down into two main categories: nuclear and chemical. Nuclear transmutation occurs within the nucleus of an atom and results in the release of energy. Chemical transmutation, on the other hand, takes place outside of the nucleus and involves the substitution of atoms.
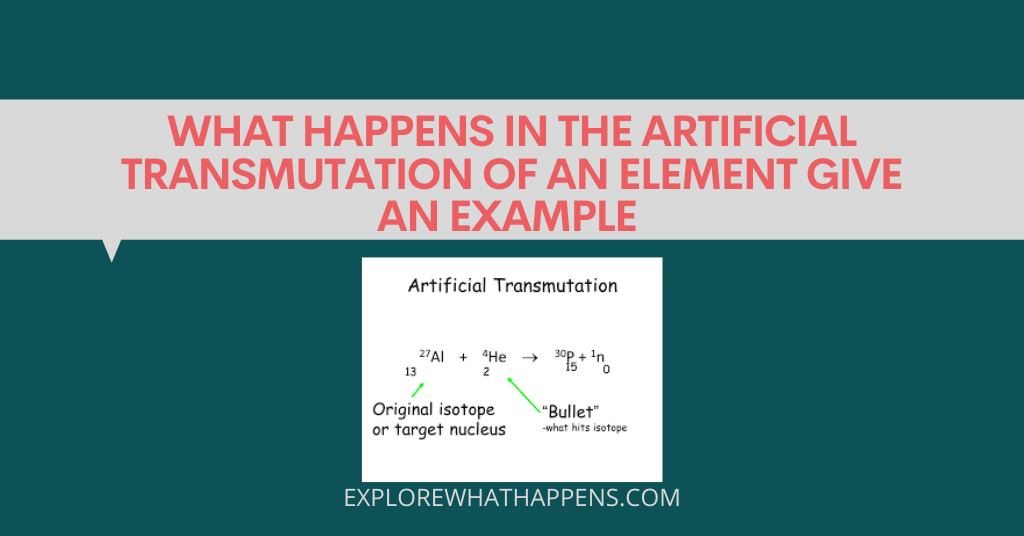
Let’s take the example of Nickel and explain it
Transmute Iron to Nickel
A scientist is looking at the properties of the chemical elements. He finds that iron has a unique property—it has the highest potential energy when it is in its most stable state. But it also has very low energy when it’s unstable. Iron has a half-life of 1.5 billion years, meaning it can stay stable for a while, but eventually it will decay into something else. The thing that iron decays into is a new element called nickel. Nickel has very similar properties to iron, but it is more stable because it doesn’t have the same chance of decaying.
What does this mean?
If we could take iron and transform it into a stable, high-energy form, we would have an element with even higher potential energy than iron, but one that won’t decay. We call this process “transmuting” or “transforming.”
How do we do it?
When iron is in its most stable state, it is in a solid-state. But if you try to change the iron into another element, the metal will be in a liquid or gas state.
You’ll need to heat up the metal until it becomes super hot, a condition called plasma. This is the same thing that happens when you burn things, like paper and wood. The process of heating up a substance to become a plasma is called “fusing.” Fusing iron with nickel is a way to transform the iron into the nickel element.
Once you fuse the two metals, you’ll need to cool it down. If you don’t, you will just have a blob of melted metal on your table.
The scientist then needs to cool the metal down. To do this, you’ll need to put the metal into a container that can hold a vacuum. A vacuum is a place where there isn’t any air pressure. This means that the metal won’t be blown around and will sit still.
Once the metal is in a vacuum, the scientist can pull out the container and get rid of the air. The metal now is in its final, stable state—a solid state. When it comes back to Earth, the metal forms a nickel nucleus. Nickel nuclei are a lot smaller than iron nuclei.
Why did the scientist do this?
Transforming iron into a different element gives the new element a higher potential energy. As long as the new element has the same number of protons, neutrons, and electrons, it will have the same properties as the element it was transformed into. The only difference is the size.
Nickel is a much smaller element than iron. That means it will have more potential energy than the iron it was formed from.
It is important to note that this is not a stable state. If iron were to remain in this state, it would still be decaying. But by creating the nickel element, you can make a stable element.
How do I know it worked?
If you look at the periodic table, you should see that iron has disappeared. Instead, you have a new element called nickel. This new element has the same number of protons
What are the four major elements of the periodic table?
The four major elements of the periodic table are hydrogen, helium, lithium, and beryllium. These elements make up over 99% of the mass of the universe. Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe, and helium is the second most common. Lithium and beryllium are both rarer elements, but are still essential for life.
What is the atomic number of copper?
The atomic number of copper is 29. This means that the nucleus of a copper atom has 29 protons. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines what element it is. Copper is a metal that is used in many electronic devices because it is a good conductor of electricity.
What is the atomic weight of copper?
The atomic weight of copper is 63.546. Atomic weight is the measure of an atom’s mass, and is determined by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Copper has 29 protons and 34 neutrons, so its atomic weight is 63.546. This means that a molecule of copper (Cu) has a mass of 63.546 atomic mass units (amu).
What is the process of artificial transmutation?
The following is a step by step process of artificial transmutation :
1. Obtain a sample of radioactive material. You can do this by either collecting it yourself or purchasing it on eBay or online auction sites.
2. Place the sample in a container and seal it tightly.
3. Shake the container vigorously to disperse the radioactive particles into the air.
4. Open the container and let the dust fall back into the container.
5. Repeat steps 2, 3 and 4 until the container is empty.
6. Place the container in a safe location.
7. Wait for an unspecified amount of time.
8. Open the container and observe.
9. If you see an emission of light, you have successfully created an atom of any desired element.
10. If you see nothing, wait longer and repeat steps 6, 7 and 8.
11. If you see a small amount of light, your experiment was unsuccessful. Try again, this time with a higher level of radioactivity.
12. If you see more light, congratulations! You’ve just created a new element.